Financial News
The Future of Uranium and its Place in the Renewable Energy Transition: Insights from Ian Timis
Uranium is a game-changer in the race towards global decarbonisation by 2050. At the heart of nuclear energy production, uranium fuels reactors that generate vast amounts of reliable, low-carbon electricity. As the world moves away from fossil fuels, nuclear power stands out as a powerful ally, offering a sustainable solution to meet our growing energy needs without emitting carbon dioxide. By harnessing the potential of uranium, we can diversify our energy sources, boost energy security, and make significant strides towards achieving our climate goals, ensuring a cleaner and greener future for generations to come.
The Pros and Cons of Investing in Uranium
The Bright Side:
Uranium possesses an energy density a million times greater than that of fossil fuels, making it an exceptionally efficient power source for nuclear reactors. Currently, there are over 440 nuclear reactors operational worldwide, with 50 more under construction, ensuring stable and potentially growing demand for uranium. By 2050, nuclear energy is expected to contribute 25% of global electricity, up from the current 10%. Moreover, uranium-powered nuclear energy emits almost 30 times less greenhouse gases than coal, providing a robust solution for countries aiming to reduce their carbon footprints. Additionally, nations with uranium resources can enhance their energy security, reducing their reliance on foreign oil and gas.
The Challenges:
However, investing in uranium is not without its difficulties. The initial capital required to build and maintain nuclear power plants can exceed $6 billion per unit. Furthermore, the disposal of nuclear waste remains a significant issue, with long-term storage solutions needed to manage radioactive materials safely for up to 10,000 years. Public perception is another challenge; incidents like the Fukushima disaster in 2011 have led to widespread scepticism and stringent regulatory hurdles. Lastly, the uranium market is known for its volatility, influenced by geopolitical factors, regulatory changes, and shifts in supply and demand.
What Drives Uranium Prices?
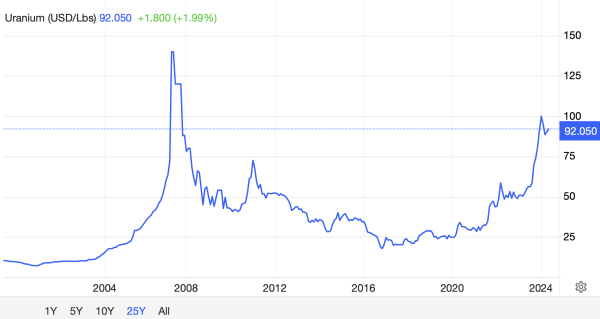
Credit: Trading Economics
Several key factors influence the price of uranium:
- Supply and Demand Dynamics: The balance between supply and demand significantly impacts uranium prices. The commissioning of new reactors typically drives demand, potentially pushing prices higher. For instance, China plans to build 150 new reactors in the next 15 years, significantly boosting demand.
- Geopolitical Events: Political instability in uranium-producing regions can disrupt supply chains, causing price fluctuations. Sanctions on major producers like Russia or Kazakhstan, which together supply over 50% of the world's uranium, can significantly impact the market.
- Regulatory Changes: Changes in nuclear energy policies, such as transitions towards renewable energy or new safety regulations, also play a crucial role in determining uranium demand and prices. For example, Japan's recent re-embrace of nuclear energy post-Fukushima has positively impacted uranium prices.
- Market Performance: Recently, the uranium market has experienced a resurgence. In 2021, uranium prices surged by over 40%, driven by increased investor interest and supply constraints. This upward trend has continued into 2023, with prices stabilising around $50 per pound, spurred by the renewed appeal of nuclear energy as a low-carbon alternative. Market analysts predict that prices could reach $70 per pound by 2025 as demand continues to grow.
- Political, Regulatory, and Ecological Considerations
Investing in uranium involves navigating a complex landscape of political, regulatory, and ecological considerations:
- Political and Regulatory Factors: Countries with stringent nuclear regulations or those aiming to phase out nuclear energy can significantly impact the uranium market. For instance, Germany's decision to shut down its nuclear reactors by 2022 has affected uranium demand across Europe. Conversely, France's commitment to nuclear power, generating 70% of its electricity from nuclear energy, provides a stable market for uranium.
Ecological Concerns: Uranium mining and nuclear waste disposal present substantial ecological challenges. In the American West, historical issues include contamination and health impacts on indigenous communities from past mining activities. Addressing these injustices and promoting sustainable mining practices are crucial for the industry's future. Modern mining techniques, like in-situ recovery, can reduce environmental impact compared to traditional methods.
Social Costs: The social costs of uranium mining, particularly in regions with indigenous populations, cannot be overlooked. Past operations have left a legacy of environmental degradation and health issues, necessitating robust regulatory frameworks and community engagement to ensure equitable and sustainable development. Recent efforts have focused on restoring affected lands and compensating communities, reflecting a growing awareness of social responsibility.
Choosing the Right Uranium Investments
When considering uranium investments, it's essential to weigh various options:
- Company Fundamentals: Scrutinise the financial health, production capacity, and management quality of uranium mining companies. Leading firms like Cameco and Kazatomprom offer stability and growth potential. Cameco, for example, produced 9,500 tonnes of uranium in 2022, making it one of the largest suppliers globally.
- Market Exposure: Uranium ETFs, such as the Global X Uranium ETF (URA), provide diversified exposure to the sector, mitigating the risk associated with individual stocks. The URA ETF has seen a 70% increase in value over the past three years, reflecting strong market performance.
- Liquidity and Volatility: Uranium futures can be highly volatile and are generally more suitable for seasoned traders. While they offer leverage, they also come with heightened risk. Futures contracts can provide significant returns during periods of rising prices but require careful market analysis and timing.
- Alternative Investment Vehicles: Besides stocks, ETFs, and futures, investors might consider uranium-focused mutual funds or direct investment in physical uranium through entities like Yellow Cake plc, which purchases and holds uranium oxide. Yellow Cake plc has increased its holdings by 50% since its inception, providing investors with direct exposure to uranium prices.
Ian Timis, the Founder of Eco Future Metals, and a distinguished figure in the mining and energy sectors, ardently advocates for the essential role of uranium in the future of energy. With over two decades of global experience, Ian has been instrumental in numerous multi-billion-dollar mining, oil, and gas projects across 15 countries spanning Africa and Europe. His extensive expertise enables him to navigate the intricacies of the mining industry's future, highlighting uranium's crucial importance in fostering a sustainable energy revolution.
Ian underscores the vital role of uranium in the future of energy. Despite the inherent challenges, the potential benefits and the pressing need for low-carbon energy solutions make uranium a compelling investment for forward-thinking investors. As the industry continues to evolve, understanding these factors will be crucial for making informed and strategic investment decisions. Ian’s insights remind us that while the road ahead may be complex, the rewards of investing in uranium are substantial, paving the way for a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
Media Contact
Company Name: Eco Future Metals
Contact Person: Ian Timis
Email: Send Email
City: London
Country: United Kingdom
Website: www.ecofuturemetals.com
More News
View More




Recent Quotes
View MoreQuotes delayed at least 20 minutes.
By accessing this page, you agree to the Privacy Policy and Terms Of Service.




